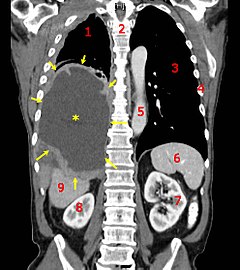
A coronal CT scan showing a malignant mesothelioma, indicated by the asterisk and the arrows.
|
|
| Focus | Cancer |
|---|---|
| Subdivisions | Medical oncology, radiation oncology, surgical oncology |
| Significant tests | Tumor markers, TNM staging, CT scans, MRI |
| Specialist | Oncologist |
Specialties
There are several sub-specialties within oncology. Moreover, oncologists often develop an interest and expertise in the management of particular types of cancer.Oncologists may be divided on the basis of the type of treatment provided or whether their role is primarily diagnostic.
- Radiology: localize, stage and often perform image-guided biopsy in order to obtain the tissue for preliminary diagnosis.
- Anatomical pathology: render the final diagnosis and prognosis of cancer, in order to guide treatment by oncologists.
- Radiation oncology: treatment primarily with radiation, a process called radiotherapy.[7]
- Surgical oncology: surgeons who specialize in tumor removal.[7]
- Medical oncology: treatment primarily with drugs, that is, pharmacotherapy, which includes chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and targeted therapy.[7][8]
- Gynecologic oncology: focuses on cancers of the female reproductive system.
- Pediatric oncology: concerned with the treatment of cancer in children
In most countries it is now common that patients are treated by a multidisciplinary team. These teams meet on a regular basis and discuss the patients under their care. These teams consist of the medical oncologist, a clinical oncologist or radiotherapist, a surgeon (sometimes there is a second reconstructive surgeon), a radiologist, a pathologist, an organ specific specialist such as a gynecologist or dermatologist, and sometimes the general practitioner is also involved. These disease oriented teams are sometimes in conflict with the general organisation and operation in hospitals. Historically hospitals are organised in an organ or technique specific manner. Multidisciplinary teams operate over these borders and it is sometimes difficult to define who is in charge.
In veterinary medicine, veterinary oncology is the sub-specialty that deals with cancer diagnosis and treatment in animals.

Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário